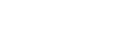연구 소개

- 연구
- 연구 소개
CloudSafe: A Tool for an Automated Security Analysis for Cloud Computing
- AI융합대학
- 2022-08-05
엄태훈 교수의 연구실에서 발표한 논문 "CloudSafe: A Tool for an Automated Security Analysis for Cloud Computing"이 "IEEE Access" 2022년 호에 게재되었다.
Cloud computing has become widely adopted by businesses for hosting applications with improved performance at a fraction of the operational costs and complexity. The rise of cloud applications has been coupled with an increase in security threat vectors and vulnerabilities. In this paper, we propose a new security assessment and enforcement tool for the cloud named CloudSafe, which provides an automated security assessment and enforce best security control for the cloud by collating various security tools. To demonstrate the applicability and usability of CloudSafe, we implemented CloudSafe and conducted security assessment in Amazon AWS. Also, we analyzed four different security countermeasure options in depth; Vulnerability Patching, Virtual Patching, Network Hardening and Moving Target Defence. Virtual Patching, Network Hardening and Moving Target Defence were determined to be feasible with regards to deployment implementation for the project. Proof of concepts were developed demonstrating the effectiveness of each feasible countermeasure option. These results indicate that the proposed tool CloudSafe is effective and efficient in helping security administrators to select optimal countermeasures to secure their cloud by conducting an in-depth security assessment.
-
Event-Based Emergency Detection for Safe Drone
지승도 교수의 연구실에서 인공지능 드론의 안전 시스템을 위한 이벤트 기반 지능 제어 기법을 연구하여 발표한 논문 "Event-Based Emergency Detection for Safe Drone"이 SCI급 국제 우수 등재 저널인 "Applied Sciences" 2022년 8월 호에 게재되었다.
2022-08-21
논문 사이트로 이동
[Figure 1] Abnormal running time with / without proposed event-based emergency detection
Quadrotor drones have rapidly gained interest recently. Numerous studies are underway for the commercial use of autonomous drones, and distribution businesses especially are taking serious reviews on drone-delivery services. However, there are still many concerns about urban drone operations. The risk of failures and accidents makes it difficult to provide drone-based services in the real world with ease. There have been many studies that introduced supplementary methods to handle drone failures and emergencies. However, we discovered the limitation of the existing methods. Most approaches were improving PID-based control algorithms, which is the dominant drone-control method. This type of low-level approach lacks situation awareness and the ability to handle unexpected situations. This study introduces an event-based control methodology that takes a high-level diagnosing approach that can implement situation awareness via a time-window. While low-level controllers are left to operate drones most of the time in normal situations, our controller operates at a higher level and detects unexpected behaviors and abnormal situations of the drone. We tested our method with real-time 3D computer simulation environments and in several cases, our method was able to detect emergencies that typical PID controllers were not able to handle. We were able to verify that our approach can provide enhanced double safety and better ensure safe drone operations. We hope our discovery can possibly contribute to the advance of real-world drone services in the near future.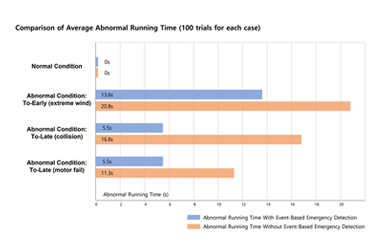
-
Research for an autonomous driving system for construction site
김필은 교수의 IRAM 연구실에서 진행중인 건설 현장을 위한 자율 주행 시스템을 연구를 소개한다. 로봇은 흔히 지도에 대한 정보를 기반으로 실내 환경에서 정확한 위치를 파악하고 탐색할 수 있다. 일반적인 지도는 건물의 구조적 레이아웃을 포함하지만 위치 파악의 정확도는 비구조적 건물 요소, 즉 문이나 가전제품 및 가구와 같은 일반적인 항목에 의해 크게 영향을 받는다. 이 연구는 센서에 의해 감지된 비구조적 요소에 대한 시맨틱맵을 동적으로 업데이트하여 실내 로봇 위치 파악의 견고성과 정확성을 향상시킨다. 우리는 객체 인식과 지도 업데이트를 전통적인 확률적 지역화로 통합하는 수정된 AMCL (Adaptive Monte Carlo Localization)을 제안한다. 제안된 접근 방식을 통해 로봇은 현재 환경 상태를 반영하는 의미론적 건물 지도을 업데이트하여 비구조적 요소로 인해 발생하는 오류를 자동으로 수정할 수 있다. kinnapped robot과 기존의 localization 시나리오에 대한 평가로 시맨틱 지도 업데이트 기능이 보다 정확하고 강력한 자세 추정을 달성할 수 있음을 보였다.
2022-06-22
[그림 1] 건설 현장을 위한 자율 주행 시스템 구조
또 다른 연구의 목적은 모의 건설현장에서 장애물을 감지할 수 있는 센서일체형 건설장비를 모의하는 것이다. 다양한 센서를 이용하여 현장을 정확히 포착하여 상황을 파악하고 상황 정보를 관리인에게 전달할 수 있는 건설장비의 완전 자율주행에 초점을 맞추고자 하였다. 3D 레이저 스캐너와 카메라를 사용하여 가상 픽업 트럭 모델을 만들고 장애물을 감지하기 위해 감지 데이터를 수집 및 처리하는 시뮬레이션에 대한 개요를 제공했다. 로봇 운영 체제(ROS) 프레임워크를 기반으로 통합된 센서를 장착한 픽업 트럭을 생성하여 포인트클라우드 클러스터를 감지하기 위해 PCL (포인트 클라우드 라이브러리) 알고리즘을 적용했다. 사각지대에 있는 작업자와 같은 물체를 인식하는 기능을 통해 혼잡한 건설 현장에서 작업자 안전을 향상시킬 수 있는 가능성을 보여준다. 추가 연구에는 실제 작업장에서 장비의 센서 기반 인식 및 평가를 기반으로 하는 자율 제어가 포함될 예정이다.