연구 소개

- 연구
- 연구 소개
해군분석모델용 AI-CGF를 위한 시나리오 생성 모델 설계(I): 진화학습
- AI융합대학
- 2022-12-01
지승도 교수의 연구실에서 해군 지능형 가상 군사(AI-CGF) 모의 기술을 연구하여 발표한 논문 "해군분석모델용 AI-CGF를 위한 시나리오 생성 모델 설계(I): 진화학습"이 "한국군사과학기술학회지" 12월호에 게재되었다. 본 연구는 워게임에서 인간 대신 AI를 접목한 최초의 시도에 대한 타당성을 검토한 연구로, 그 타당성이 충분히 입증되어 내년부터 보완 및 확장 연구를 추진할 예정이다.
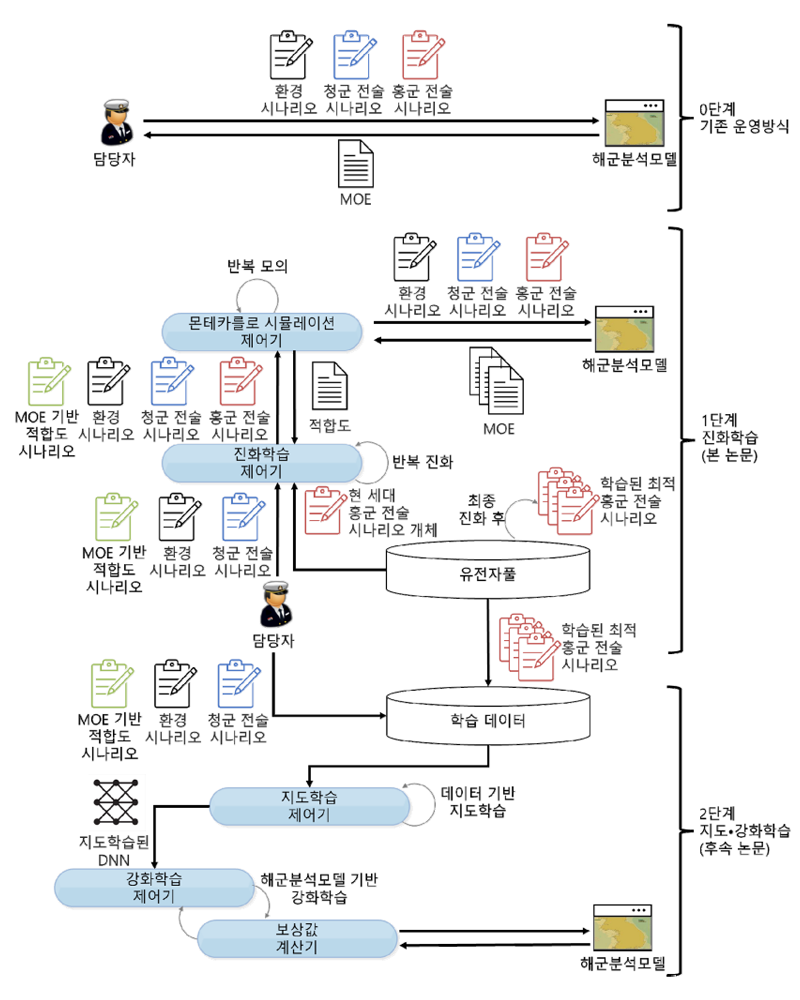
[그림 1] 전체 시스템 개요도
본 논문은 진화학습을 적용한 해군분석모델용 AI-CGF를 위한 시나리오 생성 모델을 설계하였다. 제안된 모델은 유전자 풀, 진화학습 제어기, 몬테카를로 시뮬레이션 제어기를 통해 해군분석모델에 전술 시나리오를 전달함으로써 진화학습을 시작한다. 진화 과정에서 선택, 교배, 변이의 진화 연산이 적용되었다. 총 5가지의 청군 전술 시나리오에 대하여 제안된 진화학습을 실험한 결과 전술적 가치가 높은 홍군 전술 시나리오를 생성할 수 있었다. 다만, 구성한 세력 상에서 높은 적합도가 곧바로 홍군의 승리를 의미하지는 않는 것으로 확인되었다. 그런데도 상륙전의 경우 청군의 이동 경로를 길게 가져가도록 유인함으로써 상륙 목표를 성공적으로 달성하는 고도의 전술도 확인할 수 있었다. 본 논문은 해군분석모델용 AI-CGF에 진화학습을 최초로 적용하였다. 이를 통해 인간이 설계한 청군 전술 시나리오에 대한 홍군 전술 시나리오를 자동 생성함으로써 논리적이며 수준이 높은 전술 시나리오 생성 능력을 확보할 수 있었다. 진화학습을 이용한 시나리오 생성모델은 유전 알고리즘을 통해 최적의 시나리오를 생성할 수 있다는 장점을 갖고 있으나, 학습과정에서 과도한 시간이 소요된다는 단점 또한 갖고 있다. 이를 해결하기 위해 지도 및 강화학습을 활용한 시나리오 생성 모델에 관한 연구를 후속 연구 논문에서 서술한다.
-
Extended Fusion Algorithm of A-star and Artificial Potential Field for Three-Dimensional Path Planning
최영훈 교수의 연구실에서 인공지능 드론의 3차원 비행 경로 플래닝 기술을 연구하여 발표한 논문 "Extended Fusion Algorithm of A-star and Artificial Potential Field for Three-Dimensional Path Planning"이 국제 학술 대회인 "Joint conference of APCATS, AJSAE & AAME" 2023년 10월 호에 게재되었다.
2024-01-03
논문 사이트로 이동
[Figure 1] Simulation of fusion algorithm
Urban Air Mobility (UAM) has been recently getting attention due to environmental and economic reasons. This has led to research on three-dimensional path planning requiring more degrees of freedom than traditional two-dimensional path planning. Traditional path planning algorithm such as A-star and artificial potential field has focused on how to avoid collisions and how to guarantee path’s optimality. A-star algorithm is, however, hard to handle unknown obstacles, and the artificial potential field could not reach to the given destination due to local minima problem. To relieve these issues, the fusion algorithm of A-star and artificial potential field was developed.
[Figure 2] Comparison of algorithms with known and unknown (purple) obstacles
The algorithm is, however, mainly relevant to two-dimensional path planning problems. To deal with three-dimensional path planning cases for UAM, this paper introduces an extended fusion algorithm of A-star and artificial potential field algorithms to handle three-dimensional path planning problems. To demonstrate the proposed algorithm, numerical simulations are conducted with traditional A-star and artificial potential field algorithm.
-
StARformer: Transformer with State-Action-Reward Representations for Robot Learning
이유철 교수의 Robotics and AI Navigation (RAIN) 연구실에서 발표한 논문 "StARformer: Transformer with State-Action-Reward Representations for Robot Learning"이 "IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI)"에 게재 승인되었다. 본 논문은 한국전자통신연구원(ETRI)과 미국 스토니브룩대학교(Stony Brook University)와 협업하여 강화 학습과 트랜스포머 모델을 이용한 종단간 모방학습 기반의 자율주행 기술에 관한 것으로, 이유철 교수는 이 논문의 교신 저자로 참여했다. EEE TPAMI는 세계 최고 권위의 인공지능 학술지 중 하나로, JCR 0.54%, Impact factor 24.314에 달한다. 본 논문은 2022년 12월에 출간될 예정이다.
2022-10-18
[Figure 1] StARformer System Architecture
Reinforcement Learning (RL) can be considered as a sequence modeling task, where an agent employs a sequence of past state-action-reward experiences to predict a sequence of future actions. In this work, we propose St ate- A ction- R eward Transformer ( StAR former), a Transformer architecture for robot learning with image inputs, which explicitly models short-term state-action-reward representations (StAR-representations), essentially introducing a Markovian-like inductive bias to improve long-term modeling. StARformer first extracts StAR-representations using self-attending patches of image states, action, and reward tokens within a short temporal window. These StAR-representations are combined with pure image state representations, extracted as convolutional features, to perform self-attention over the whole sequence. Our experimental results show that StARformer outperforms the state-of-the-art Transformer-based method on image-based Atari and DeepMind Control Suite benchmarks, under both offline-RL and imitation learning settings. We find that models can benefit from our combination of patch-wise and convolutional image embeddings. StARformer is also more compliant with longer sequences of inputs than the baseline method. Finally, we demonstrate how StARformer can be successfully applied to a real-world robot imitation learning setting via a human-following task.
[Figure 2] Imitation Learning based Scenario Experiments to Evaluate the StARformer Navigation Performance
This study introduces StARformer, which explicitly models strong local relations (Step Transformer) to facilitate the long-term sequence modeling (Sequence Transformer) in Visual RL. Our extensive empirical results show how the learned StAR-representations help our model to outperform the baseline in both Atari and DMC environments, as well as both offline RL and imitation learning settings. We find that the fusion of learned StAR-representations and convolution features benefits action prediction. We further demonstrate that our designed architecture and token embeddings are essential to successfully model trajectories, with an emphasis on long sequences. We also verify that our method can be applied to real-world robot learning settings via a human-following experiment.