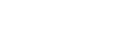연구 소개

- 연구
- 연구 소개
Amnesia as a Catalyst for Enhancing Black Box Pixel Attacks in Image Classification and Object Detection
- SW중심대학 사업단
- 2024-11-17
정재훈 교수의 연구실에서 발표한 "Amnesia as a Catalyst for Enhancing Black Box Pixel Attacks in Image Classification and Object Detection" 논문이 이번 2024년 "NeurIPS (Neural Information Processing Systems)"에 게재되었다. 본 논문은 강화학습 기반의 블랙박스 픽셀 공격 기법(RFPAR)을 통해, 기존 이미지 분류 및 객체 탐지에서 사용되는 적대적 공격 기법을 개선, 적대적 이미 생성 뿐만 아니라 객체 탐지 분야에서도 혁신적인 성능 개선을 달성했다.
NeurIPS는 1987년 창립된 이래 인공지능 및 기계학습 분야에서 가장 권위 있는 학회 중 하나로, 매년 전 세계 연구자들이 최첨단 연구 성과를 발표하고 토론하는 자리이다. 이번 2024년 학회에는 인공지능 학계와 업계의 관심을 받는 최신 연구들이 발표될 예정이며, 논문 선정이 매우 까다롭기로 유명하다.
It is well known that query-based attacks tend to have relatively higher success rates in adversarial black-box attacks. While research on black-box attacks is ac- tively being conducted, relatively few studies have focused on pixel attacks that target only a limited number of pixels. In image classification, query-based pixel attacks often rely on patches, which heavily depend on randomness and neglect the fact that scattered pixels are more suitable for adversarial attacks. Moreover, to the best of our knowledge, query-based pixel attacks have not been explored in the field of object detection. To address these issues, we propose a novel pixel-based black-box attack called Remember and Forget Pixel Attack using Reinforcement Learning(RFPAR), consisting of two main components: the Remember and For- get processes. RFPAR mitigates randomness and avoids patch dependency by leveraging rewards generated through a one-step RL algorithm to perturb pixels. RFPAR effectively creates perturbed images that minimize the confidence scores while adhering to limited pixel constraints. Furthermore, we advance our pro- posed attack beyond image classification to object detection, where RFPAR re- duces the confidence scores of detected objects to avoid detection. Experiments on the ImageNet-1K dataset for classification show that RFPAR outperformed state-of-the-art query-based pixel attacks. For object detection, using the MS- COCO dataset with YOLOv8 and DDQ, RFPAR demonstrates comparable mAP reduction to state-of-the-art query-based attack while requiring fewer query. Fur- ther experiments on the Argoverse dataset using YOLOv8 confirm that RFPAR effectively removed objects on a larger scale dataset. Our code is available at https://github.com/KAU-QuantumAILab/RFPAR.
-
P2P-Fed: A Decentralized Federated Learning Platform on Structured Peer-to-peer Systems
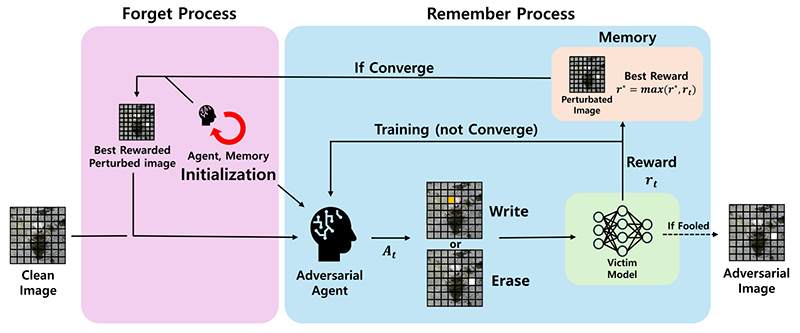
이재환 교수의 연구실에서 발표한 "P2P-Fed: A Decentralized Federated Learning Platform on Structured Peer-to-peer Systems" 논문이 이번 2025년 "CCGrid 2025(The 25th IEEE Interational Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and lnternet Computing)"의 정규논문으로 채택되었다. 본 논문은 최근 인공지능 분야에서 주목받고 있는 연합학습(Federated Learning, 데이터를 중앙 서버에 모으지 않고 각 기기에서 따로 학습해 결과만 공유하는 AI 학습 방식)의 구조적 한계를 해결하기 위해, 토렌트나 블록체인 기술에도 활용되는 Peer-to-Peer(P2P) 네트워크 기반의 분산해시테이블(DHT·Distributed Hash Table, 정보를 여러 컴퓨터에 분산시켜 저장하고 효율적으로 찾는 기술)을 활용한 구조를 제안하였다. 특히 Chord 프로토콜(데이터 저장 위치를 원형 구조로 정하고 빠르게 찾는 방식)을 활용한 완전 분산 학습 구조를 설계하고 구현해냈다는 점에서 의미가 큰 연구다.
2025-06-02
기존의 연합학습 방식은 중앙 서버가 필요하거나, 모든 기기가 서로 직접 통신해야 해서 기기 수가 늘어나면 통신량도 커지는 문제가 있었다. 반면 이번에 제안된 방식은 각 기기가 수평적으로 연결된 P2P 네트워크 상에서 직접 통신하며 학습결과를 공유하도록 설계되어, 중앙 서버 없이도 높은 확장성과 안정성을 확보할 수 있다. 이는 통신량을 줄이고 동적인 네트워크 환경(high-churn network)나 이기종 장치 환경에서도 연합학습이 안정적으로 수행되는 효과를 가져온다.
특히, 연합학습에 참여하는 노드 수가 N개일 때, 하나의 노드가 모든 노드와 N회 통신되야 하는 기존의 방식과 달리, 노드 수가 많아져도 통신 횟수가 logN회 수준으로 줄어들어 대규모 환경에서의 효율성이 극대화된다는 것을 입증했다. 실제로 80개의 노드가 동시에 통신하는 실험 환경에서, 연구팀이 제안한 알고리즘은 기존 최고 성능 기법에 비해 정확도는 최대 6.9% 향상, 통신량은 약 23% 감소라는 성과를 나타냈다. 이는 스마트폰, 웨어러블 장치, 자율주행시스템, 저궤도 위성 네트워크처럼 다양한 디바이스가 동시에 연결되는 미래 AI 서비스 환경에서 핵심 기술로 다양하게 활용될 가능성을 보여준다.
[그림 1] DHT 기반 Chord 적용 분산 연합학습 구조
Federated learning is a distributed deep learning method that trains models without sending local private training data to a server, achieving communication efficiency and security. However, current federated learning techniques have two key issues: 1) scalability limitations due to heavy traffic concentrated on the central server and 2) performance degradation caused by systems and data heterogeneity. To address these issues, we propose P2P-Fed, a decentralized federated learning approach with asynchronous aggregation to minimize delays and enhance concurrency for faster convergence. We adopt Chord, a popular distributed hash table protocol, to reduce the load on individual nodes in large-scale environments and ensure stable performance in high-churn networks. We designed and implemented this system to run in a real distributed environment. Experiments in various realistic scenarios demonstrated that P2P-Fed achieved up to a 6.9% performance improvement compared to the best-performing baseline algorithm, without incurring additional overhead.
-
Extended Fusion Algorithm of A-star and Artificial Potential Field for Three-Dimensional Path Planning
최영훈 교수의 연구실에서 인공지능 드론의 3차원 비행 경로 플래닝 기술을 연구하여 발표한 논문 "Extended Fusion Algorithm of A-star and Artificial Potential Field for Three-Dimensional Path Planning"이 국제 학술 대회인 "Joint conference of APCATS, AJSAE & AAME" 2023년 10월 호에 게재되었다.
2024-01-03
논문 사이트로 이동
[Figure 1] Simulation of fusion algorithm
Urban Air Mobility (UAM) has been recently getting attention due to environmental and economic reasons. This has led to research on three-dimensional path planning requiring more degrees of freedom than traditional two-dimensional path planning. Traditional path planning algorithm such as A-star and artificial potential field has focused on how to avoid collisions and how to guarantee path’s optimality. A-star algorithm is, however, hard to handle unknown obstacles, and the artificial potential field could not reach to the given destination due to local minima problem. To relieve these issues, the fusion algorithm of A-star and artificial potential field was developed.
[Figure 2] Comparison of algorithms with known and unknown (purple) obstacles
The algorithm is, however, mainly relevant to two-dimensional path planning problems. To deal with three-dimensional path planning cases for UAM, this paper introduces an extended fusion algorithm of A-star and artificial potential field algorithms to handle three-dimensional path planning problems. To demonstrate the proposed algorithm, numerical simulations are conducted with traditional A-star and artificial potential field algorithm.