연구 소개

- 연구
- 연구 소개
P2P-Fed: A Decentralized Federated Learning Platform on Structured Peer-to-peer Systems
- SW중심대학 사업단
- 2025-06-02
이재환 교수의 연구실에서 발표한 "P2P-Fed: A Decentralized Federated Learning Platform on Structured Peer-to-peer Systems" 논문이 이번 2025년 "CCGrid 2025(The 25th IEEE Interational Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and lnternet Computing)"의 정규논문으로 채택되었다. 본 논문은 최근 인공지능 분야에서 주목받고 있는 연합학습(Federated Learning, 데이터를 중앙 서버에 모으지 않고 각 기기에서 따로 학습해 결과만 공유하는 AI 학습 방식)의 구조적 한계를 해결하기 위해, 토렌트나 블록체인 기술에도 활용되는 Peer-to-Peer(P2P) 네트워크 기반의 분산해시테이블(DHT·Distributed Hash Table, 정보를 여러 컴퓨터에 분산시켜 저장하고 효율적으로 찾는 기술)을 활용한 구조를 제안하였다. 특히 Chord 프로토콜(데이터 저장 위치를 원형 구조로 정하고 빠르게 찾는 방식)을 활용한 완전 분산 학습 구조를 설계하고 구현해냈다는 점에서 의미가 큰 연구다.
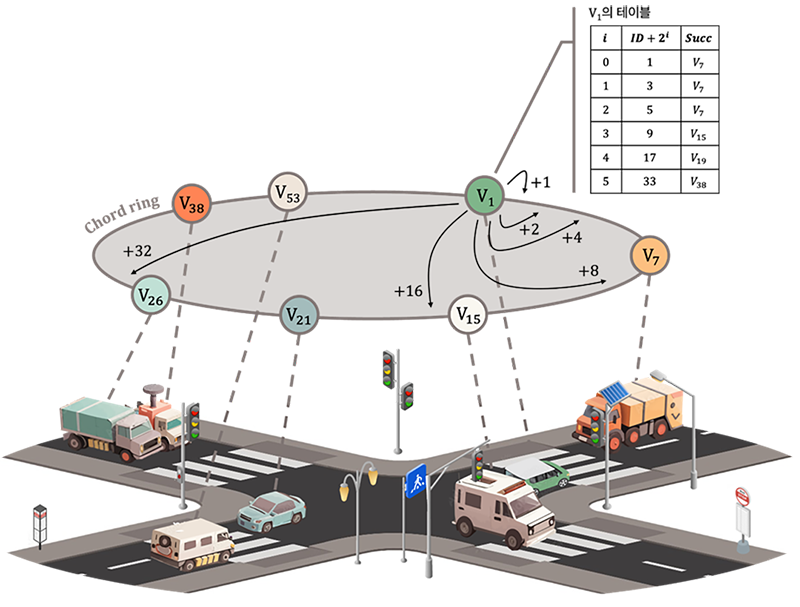
Federated learning is a distributed deep learning method that trains models without sending local private training data to a server, achieving communication efficiency and security. However, current federated learning techniques have two key issues: 1) scalability limitations due to heavy traffic concentrated on the central server and 2) performance degradation caused by systems and data heterogeneity. To address these issues, we propose P2P-Fed, a decentralized federated learning approach with asynchronous aggregation to minimize delays and enhance concurrency for faster convergence. We adopt Chord, a popular distributed hash table protocol, to reduce the load on individual nodes in large-scale environments and ensure stable performance in high-churn networks. We designed and implemented this system to run in a real distributed environment. Experiments in various realistic scenarios demonstrated that P2P-Fed achieved up to a 6.9% performance improvement compared to the best-performing baseline algorithm, without incurring additional overhead.