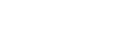연구 소개

- 연구
- 연구 소개
On the confidence of stereo matching in a deep-learning era
- AI융합대학
- 2021-04-02
김선옥 교수의 연구실에서 발표한 논문 "On the confidence of stereo matching in a deep-learning era: a quantitative evaluation"이 "IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence"에 게재되었다.
[그림 1] KITTI 2015 및 Middlebury 데이터셋으로 시험한 Qualitative results concerning Census-CBCA 알고리즘
본 논문은 스테레오 매칭을 획득한 깊이 영상의 신뢰도 추정 방법들을 분석한 논문으로 최근 머신러닝 분야의 세계 최고 학술지인 IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (Impact factor: 16.389) 에 게재 승인 받았다. 본 연구는 이탈리아의 볼로냐 대학교(University of Bologna) 연구진과 국내 한국항공대학교, 연세대학교, 고려대학교, 이화여자대학교의 공동 연구로 진행되었으며 기존의 handcrafted feature부터 최근 사용되고 있는 deep learning 기반의 방법 등 약 60여가지 이상의 신뢰도 추정 방법에 대한 실험을 진행하여 결과를 비교 및 분석하였다.
분석 결과, 2019년 세계 최고 컴퓨터비전 학술대회인 IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)에서 발표된 김선옥 교수의 ‘LAF-Net: Locally Adaptive Fusion Networks for Stereo Confidence Estimation”이 신뢰도 추정에 있어서 가장 뛰어난 성능을 보여줌을 확인하였다.
-
Automatic incremental recomposition algorithm for QoS-aware internet of things service composition
길현영 교수의 연구실에서 발표한 논문 "Automatic incremental recomposition algorithm for QoS-aware internet of things service composition"이 "International Journal of Web and Grid Services 2021"에 게재되었다.
2021-07-16
논문 사이트로 이동
웹서비스(Web service)는 웹 기술을 기반으로 하여 machine-to-machine inter-operation을 제공하기 위한 소프트웨어 시스템으로, 서비스 지향 아키텍쳐 (Service-Oriented Architecture)의 서비스(독립적 기능을 가질 수 있는 비즈니스 논리의 기본 단위)를 기본 개념으로 하여 현실화한 기술이다. 현재 웹서비스는 분산시스템이나 Web 환경에서 Service provider가 다수의 client에게 자신의 기능을 사용할 수 있도록 지원하는 Web API 서비스의 형태로 많이 사용되고 있다. 또한 사물인터넷(Internet-of-Things, IoT) 관련한 다수의 연구에서도 각각의 사물의 기능을 하나의 웹 기반 서비스로서 구현하고 상위 구조에서 이러한 서비스 집합을 관리하는 서비스 지향 아키텍쳐 기반 방식을 사용함으로써 좀더 효율성있는 시스템을 구현, 사용한다. 사용자가 원하는 요구사항을 하나의 특정 서비스로 완전히 충족시키지 못하는 경우, 여러 개의 웹서비스들을 합성하게 함으로써 해당 요구사항을 만족시키는 서비스 컴포지션(Service Composition) 기법은 서비스 개발 비용을 낮추고 효율성을 높이는 기법이다. Web 기반의 large scaled computing 환경과 컴퓨팅 리소스가 한정적인 다양한 종류의 IoT 기기 환경에서, 이러한 서비스 컴포지션 문제는 그 활용성이 더욱 높다.
그런데, 다양한 기기들과 자원 한계성을 갖는 IoT 서비스 환경에서는 일시적인 서버 다운, 시스템 과부하, 네트워크 불량 등의 환경적 변화가 발생할 수 있다. 이러한 변화가 발행하였을 때 기존 service composition 문제의 조건이 변하였기 때문에 그 전에 생성한 composite web service는 더 이상 최적의 solution으로 유효하지 못하다. 특히, QoS를 고려하는 service compositon 문제는 사용자가 원하는 목적을 달성하면서도 최적의 QoS값을 갖는 composite service를 구하는 문제로서, 일부의 환경적 조건 변화 때문에 전체 문제를 처음부터 고려하여 최적의 QoS 값을 갖는 솔루션을 찾는 것은 컴퓨팅 시간의 낭비를 초래하게 된다.
[그림 1] Emergency response system
본 논문에서는 환경의 변화가 발생하였을 때 QoS를 고려하는 service compositon 문제를 처음부터 다시 풀지 않고 이전 풀이에서의 중간 과정을 최대한 활용하여 최적의 솔루션을 효율적으로 찾아낼 수 있는 incremental re-composition algorithm을 제안하였다. 본 연구에서 제안한 알고리즘은 특히 적은 변화율을 갖는 경우에 기존 알고리즘에 비해 매우 빠르게 최적의 composite service를 찾아냈고, 다수의 경우에서 변화율의 증가에 따라 computing 시간의 선형적 증가세를 보임으로써, 그 효율성을 보였다.
본 연구실은 다양한 네트워크 환경에서 Web- 및 IoT-서비스의 효율적 사용을 위한 자동화된 service discovery & composition에 대한 연구를 AI planning, model checking, Graph theory 기반 기술을 사용하여 진행해왔고, 최근에는 GNN(Graph Neural Network)을 기반으로 Service representation learning 연구와 Stock/Bitcoin price movement prediction에 대한 연구를 진행 중이다.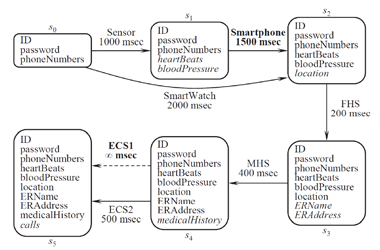
-
A Framework for Real-Time Intrusion Response in Software Defined Networking Using Precomputed Graphical Security Models
엄태훈 교수의 연구실에서 발표한 논문 "A Framework for Real-Time Intrusion Response in Software Defined Networking Using Precomputed Graphical Security Models"이 "Security and Communication Networks (SCN)" 2020년 호에 게재되었다.
2020-02-18
논문 사이트로 이동
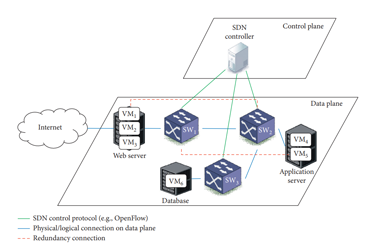
[Figure 1] Framework for real-time intrusion response in SDN
Software Defined Networking (SDN) has been adopted in many application domains, as it provides functionalities to dynamically control the network flow, more robust, and more economical compared to the traditional networks. In order to strengthen the security of the SDN against cyber attacks, many security solutions have been proposed. However, those solutions need to be compared in order to optimize the security of the SDN. To assess and evaluate the security of the SDN systematically, one can use graphical security models (e.g., Attack Graphs and Attack Trees). However, it is difficult to provide defense against an attack in real time due to their high computational complexity. In this paper, we propose a real-time intrusion response in SDN using precomputation to estimate the likelihood of future attack paths from an ongoing attack. We also take into account various SDN components to conduct a security assessment, which were not available when addressing only the components of an existing network. Our experimental analysis shows that we are able to estimate possible attack paths of an ongoing attack to mitigate it in real-time, as well as showing the security metrics that depend on the flow table corresponding to the attack considering the SDN component . Hence, the proposed approach can be used to provide effective real-time mitigation solutions for securing SDN.